In the realm of fluid control and automation, solenoid valves play a crucial role in regulating the flow of liquids and gases. Among the various types of solenoid valves, the pulse solenoid valve stands out for its unique functionality and applications. This article aims to delve into the basic concepts, working principles, differences from regular solenoid valves, and the various types of pulse solenoid valves available.
What is a Pulse Solenoid Valve?
A pulse solenoid valve is a specialized type of solenoid valve designed to control fluid flow in a pulsating manner. Unlike traditional solenoid valves that maintain a continuous flow or no flow at all, a pulse solenoid valve operates by rapidly opening and closing its valve orifice in a controlled sequence. This pulsating action is achieved through the use of an electromagnetic coil that generates a magnetic field when energized, causing the valve to open and close at specific intervals.
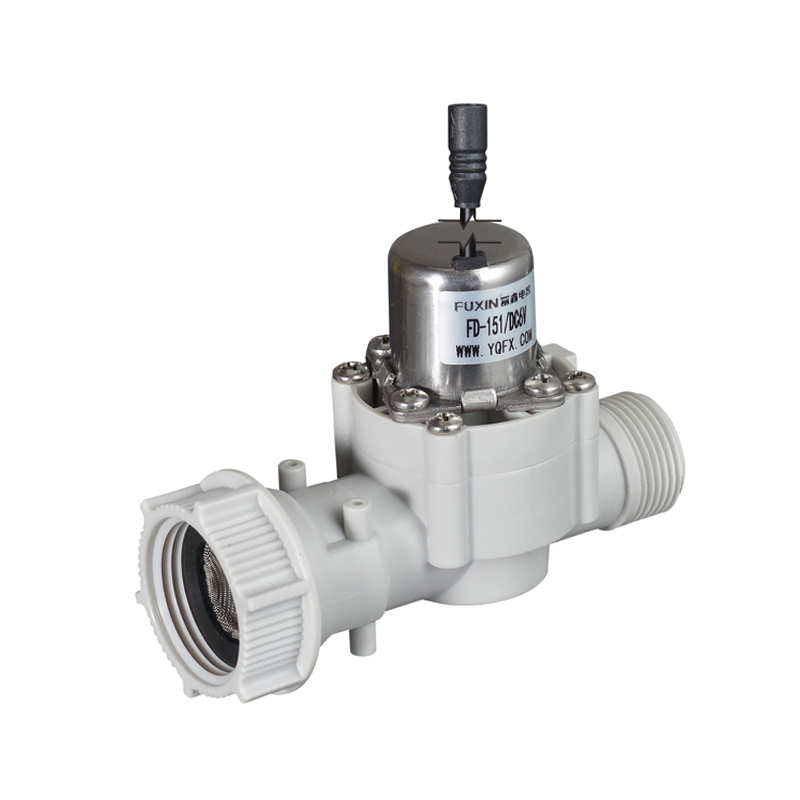

The pulse solenoid valve is particularly useful in applications where precise control of fluid flow is required. For example, in fuel injection systems for internal combustion engines, a pulse solenoid valve can accurately control the amount of fuel injected into the engine cylinders by regulating the duration and frequency of the pulses. This precise control helps optimize fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance engine performance.
How Does a Pulse Solenoid Valve Work?
The working principle of a pulse solenoid valve is based on the interaction between an electromagnetic coil and a movable valve core. When an electrical current is applied to the coil, it generates a magnetic field that attracts the valve core, causing the valve to open. When the current is interrupted, the magnetic field collapses, and the valve core is pushed back to its original position by a spring or other mechanical means, closing the valve.
In a pulse solenoid valve, the electrical current is applied in short bursts or pulses, rather than continuously. This pulsing action allows for precise control of the valve's opening and closing. The frequency and duration of the pulses can be adjusted to achieve the desired flow rate and pattern. For instance, a higher pulse frequency will result in a higher flow rate, while a lower frequency will reduce the flow rate.
The pulse solenoid valve typically consists of several key components, including the solenoid coil, valve core, valve seat, and spring. The solenoid coil is the heart of the valve, responsible for generating the magnetic field. The valve core is a movable component that interacts with the magnetic field to open and close the valve. The valve seat is the surface against which the valve core seals to prevent fluid flow when the valve is closed. The spring provides the necessary force to return the valve core to its closed position when the magnetic field is removed.
Differences Between a Pulse Solenoid Valve and a Regular Solenoid Valve
While both pulse solenoid valves and regular solenoid valves utilize electromagnetic principles to control fluid flow, there are several key differences between the two:
1. Flow Control Mechanism
A regular solenoid valve operates in a binary manner, either fully open or fully closed. When the solenoid coil is energized, the valve opens, allowing fluid to flow through. When the coil is de-energized, the valve closes, stopping the flow. In contrast, a pulse solenoid valve controls flow through a series of rapid pulses, allowing for more precise and variable flow control.
2. Application Suitability
Regular solenoid valves are well-suited for applications where a simple on/off control is sufficient, such as in irrigation systems, where water flow needs to be turned on or off at specific times. Pulse solenoid valves, on the other hand, are ideal for applications requiring precise and dynamic flow control, such as in fuel injection systems, where the amount of fuel injected needs to be finely tuned for engine performance.
3. Complexity and Cost
Pulse solenoid valves are generally more complex and expensive than regular solenoid valves. The additional components and control mechanisms required to achieve pulsating flow add to the cost and complexity of the valve. However, the benefits of precise flow control often justify the higher cost in applications where performance and efficiency are critical.
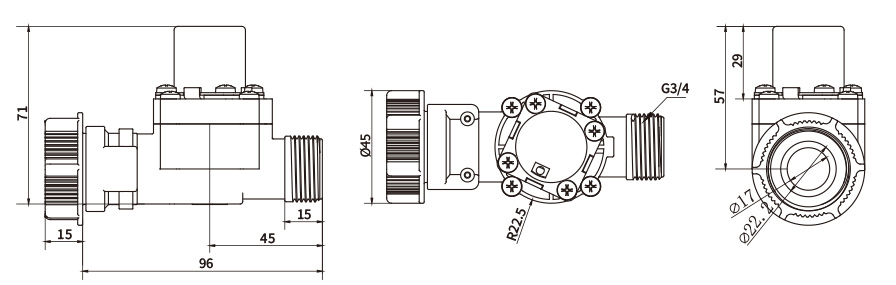
Types of Pulse Solenoid Valves
Pulse solenoid valves can be categorized based on their default state when not energized. The two main types are normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) valves.
Normally Open Pulse Solenoid Valves
A normally open pulse solenoid valve is designed to allow fluid flow when the solenoid coil is not energized. In this state, the valve core is held open by a spring or other mechanical means. When the coil is energized, the magnetic field generated attracts the valve core, closing the valve and stopping the flow. This type of valve is useful in applications where fluid flow is required of the time, and the valve needs to be closed only during specific intervals.
Normally Closed Pulse Solenoid Valves
A normally closed pulse solenoid valve, as the name suggests, is closed when the solenoid coil is not energized. In this state, the valve core is held against the valve seat by a spring or other mechanical means, preventing fluid flow. When the coil is energized, the magnetic field generated lifts the valve core, opening the valve and allowing fluid to flow. This type of valve is commonly used in applications where fluid flow needs to be controlled and regulated, such as in fuel injection systems.
Hybrid Pulse Solenoid Valves
In addition to the basic normally open and normally closed types, there are also hybrid pulse solenoid valves that can be configured to operate in either mode. These valves offer greater flexibility and can be adapted to various applications by simply adjusting the control settings.
Pulse solenoid valves represent a significant advancement in fluid control technology, offering precise and dynamic flow control through their pulsating action. By understanding the basic concepts, working principles, and differences from regular solenoid valves, engineers and technicians can better select and apply these valves in various industrial and automotive applications. Whether used in fuel injection systems, hydraulic circuits, or other fluid control applications, pulse solenoid valves play a vital role in optimizing performance, efficiency, and reliability. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements and innovations in the design and functionality of pulse solenoid valves, making them even more versatile and effective tools in the field of fluid control.

 EN
EN English
English Español
Español