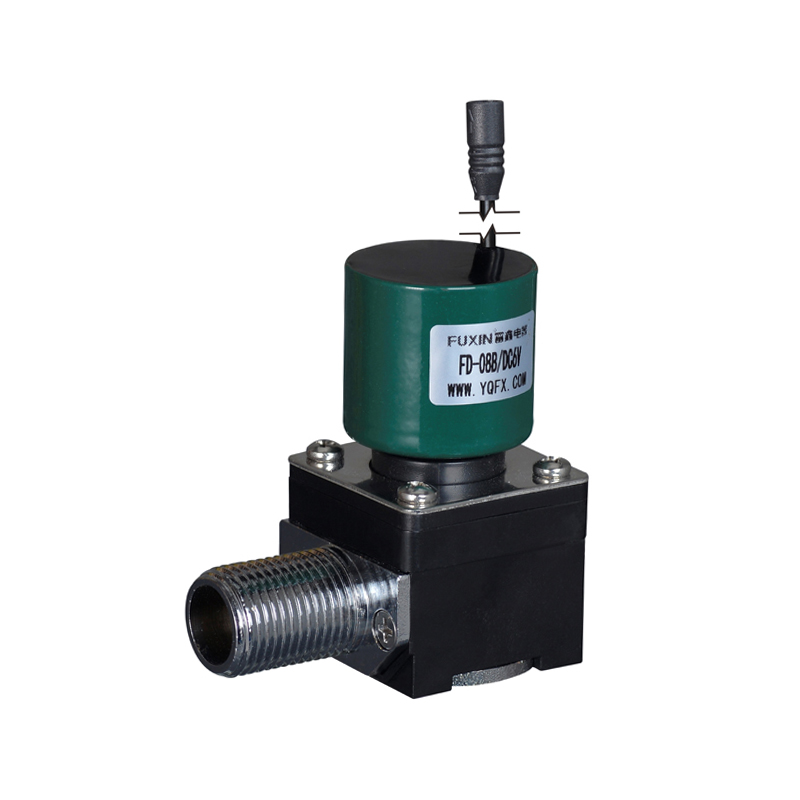
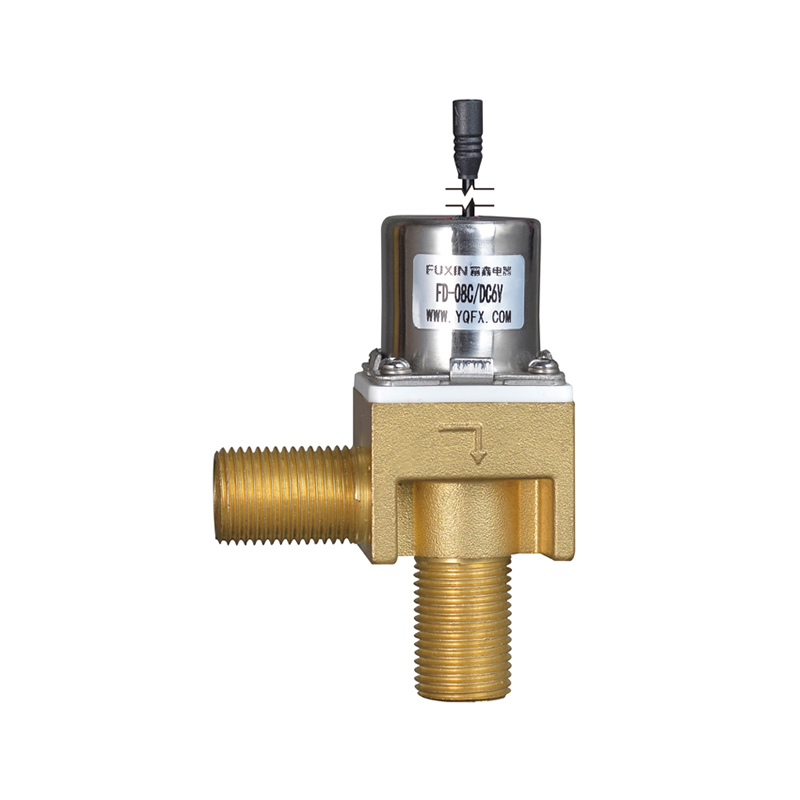
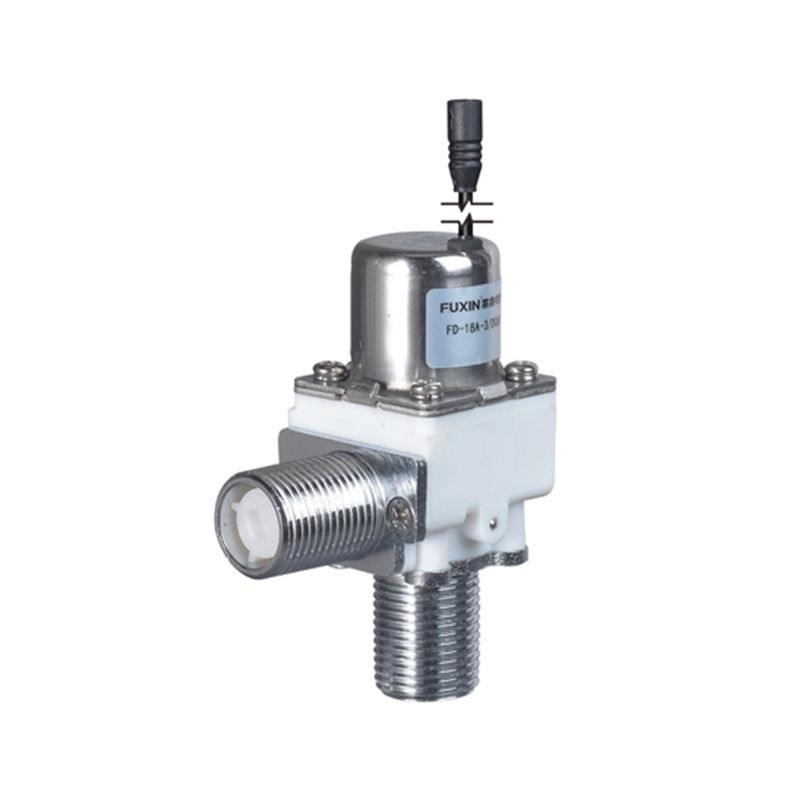
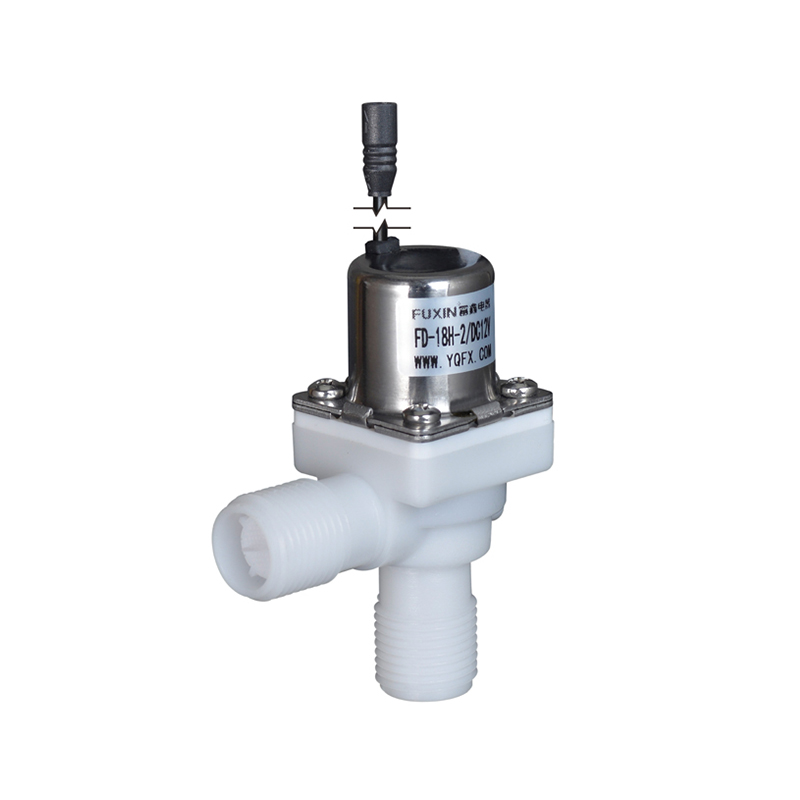
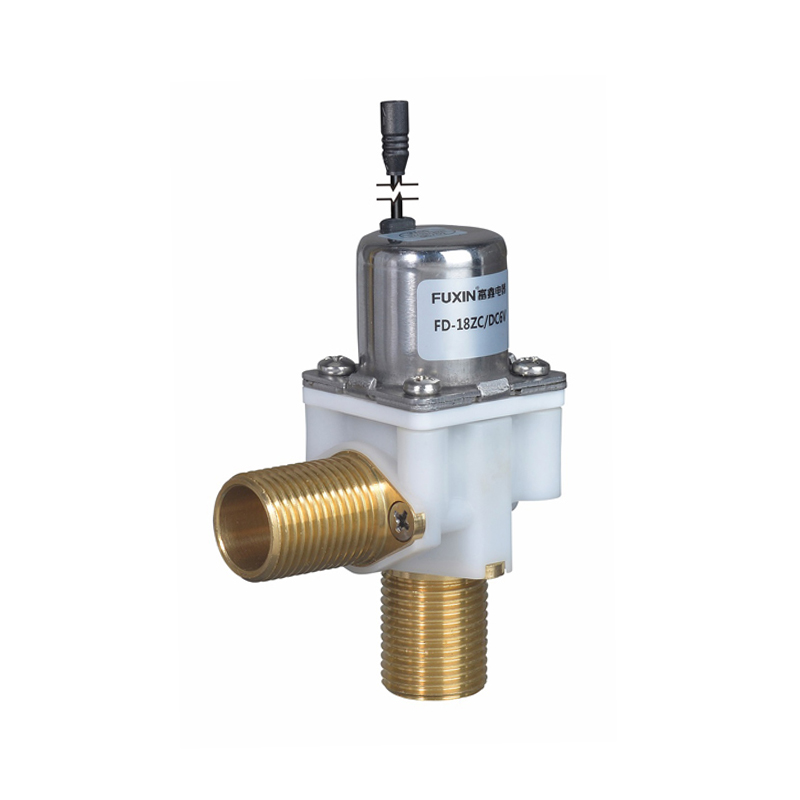
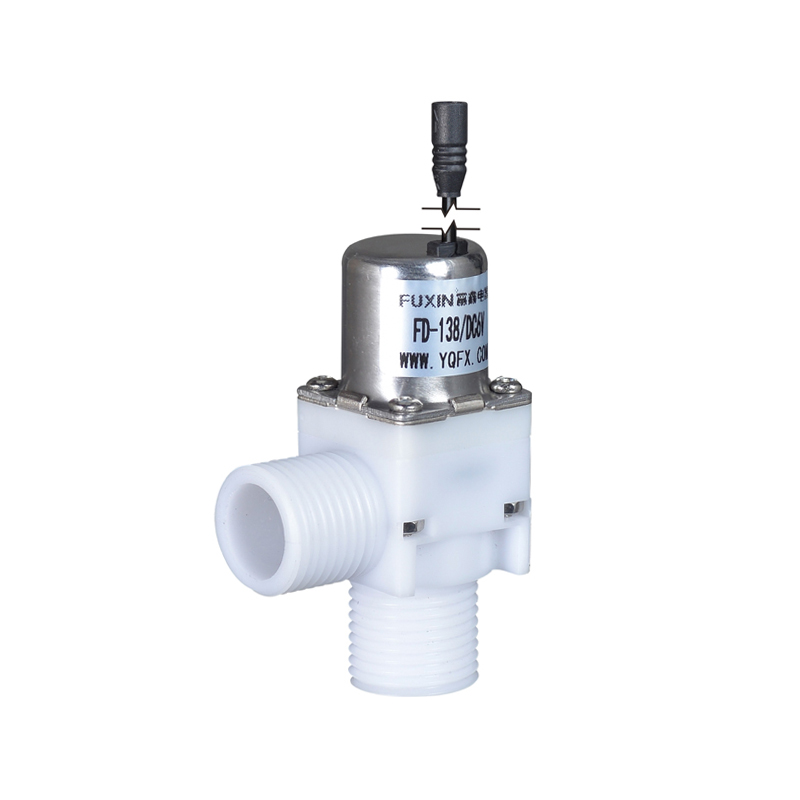
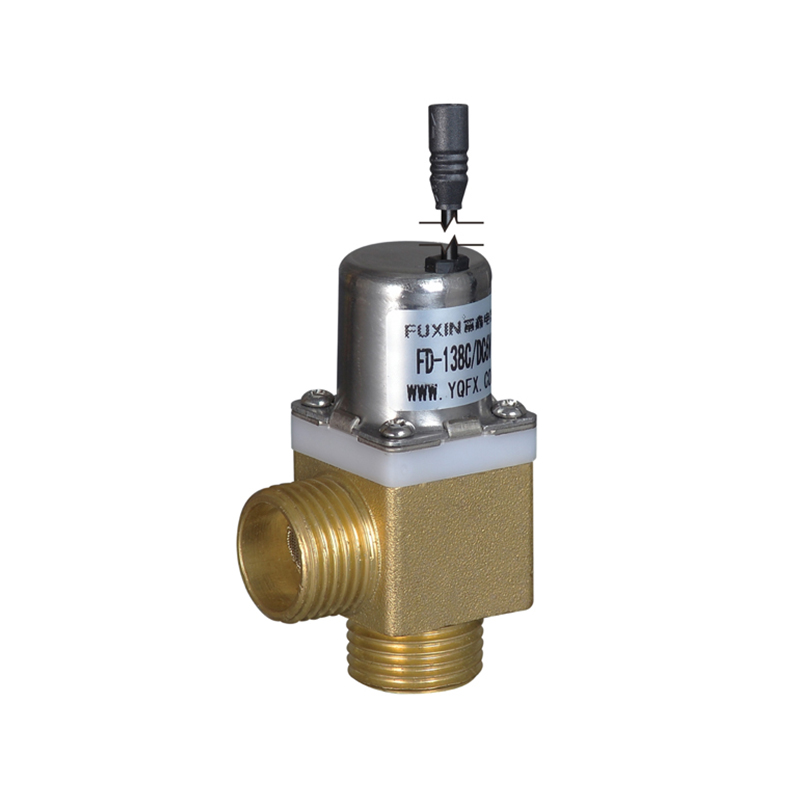
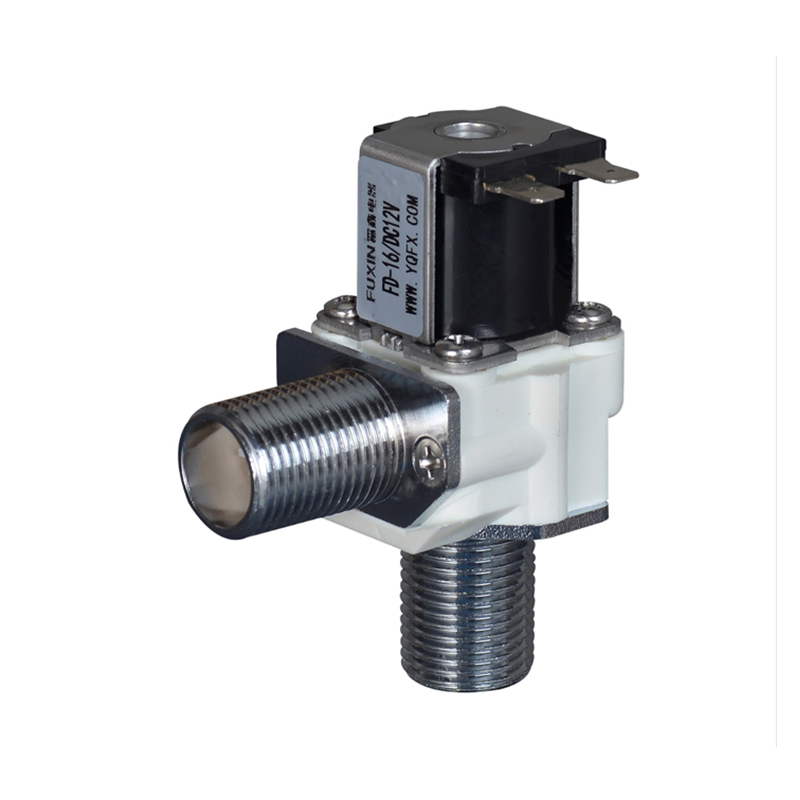
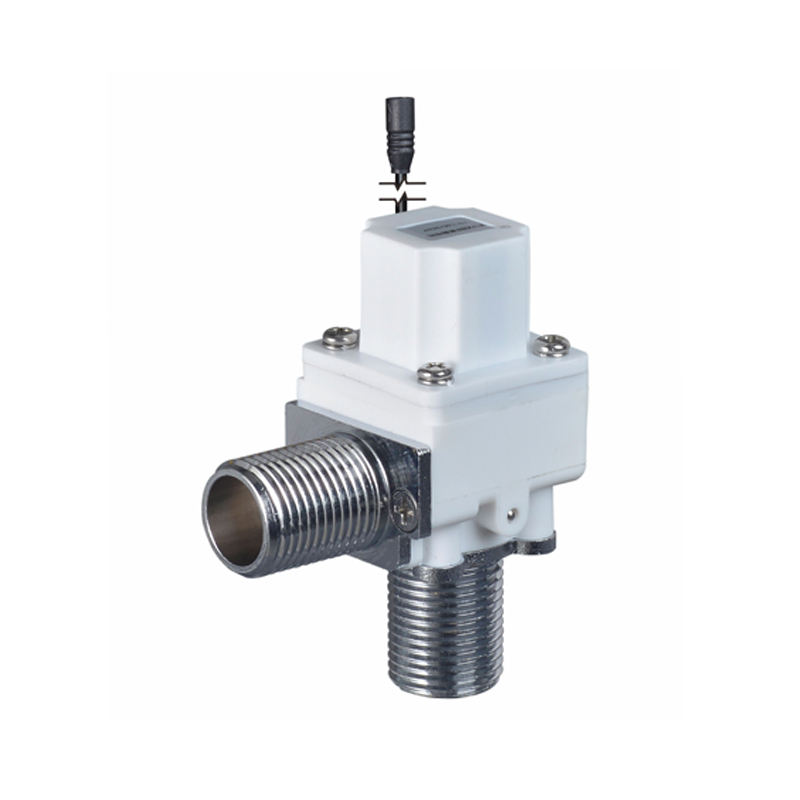
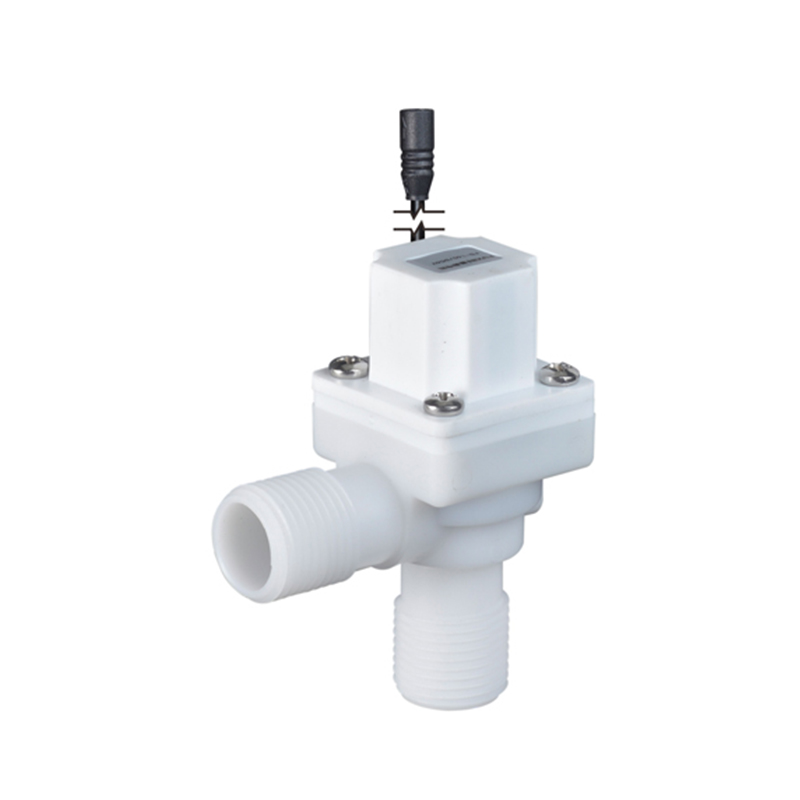
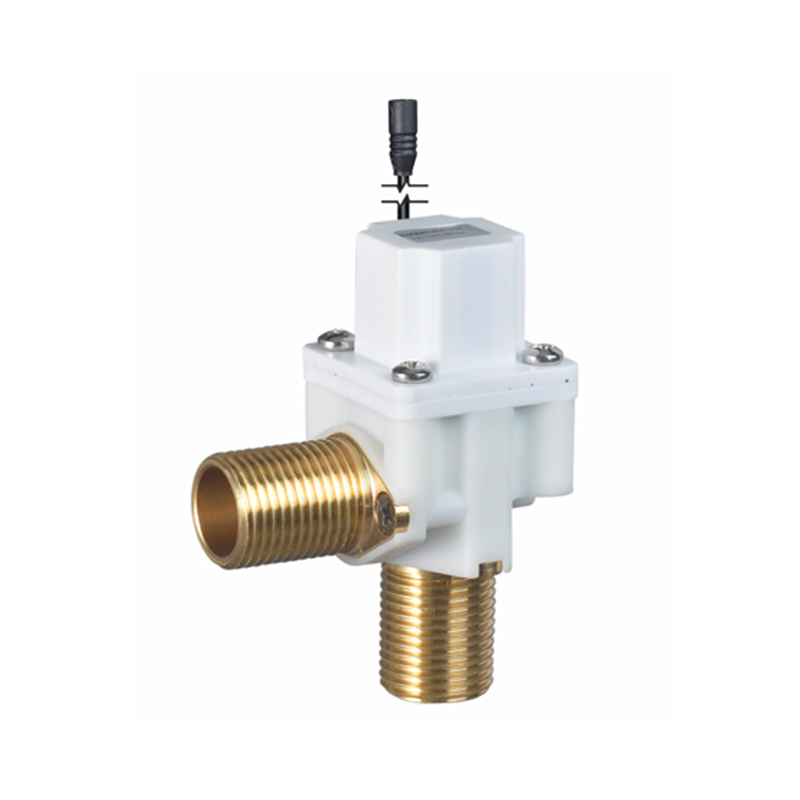
The Pulse Solenoid Valve plays a critical role in modern industrial dust removal systems, particularly within baghouse filters and pneumatic systems. Unlike standard solenoid valves that rely on continuous power to maintain their operational state, the Pulse Solenoid Valve operates through a momentary electrical pulse, triggering a quick and forceful release of compressed air. This article explores the inner workings of the Pulse Solenoid Valve, how it utilizes electromagnetic force for rapid switching, and how it differs fundamentally from conventional solenoid valve technology.
At the core of a Pulse Solenoid Valve is its ability to use short bursts of electrical energy to control high-pressure air flows. When an electrical pulse is sent to the coil, it generates an electromagnetic field that pulls the armature or plunger upward. This action briefly opens the valve and allows a surge of compressed air to exit through the outlet. As soon as the pulse ends, the electromagnetic field collapses, and a return spring pushes the armature back to its resting position, sealing the valve shut. This rapid on-off motion is highly efficient for applications where brief, timed bursts of air are required, particularly for cleaning dust collector filters.
Unlike traditional solenoid valves, which remain open or closed as long as voltage is applied, the Pulse Solenoid Valve needs only a single, short-duration signal to change its state. This pulse-driven mechanism reduces energy consumption, minimizes coil heating, and significantly extends the valve’s operational life. It also enables better control in sequential dust cleaning systems, where multiple valves need to open and close in a carefully timed cycle.
One of the common applications of the Pulse Solenoid Valve is in pulse-jet baghouse dust collectors. In such systems, the valve connects a compressed air tank to a blow tube above a row of filter bags. When the Pulse Solenoid Valve opens, a high-pressure air blast is released, traveling down the tube and dislodging dust from the filter surfaces. The quick and forceful nature of this air pulse is essential for maintaining filter performance and air permeability.
The Pulse Solenoid Valve is typically controlled by a timer or PLC (programmable logic controller), which determines the duration and interval between pulses. This precision control ensures that dust removal is efficient without wasting energy or overloading the system. The valve's diaphragm and internal flow path are specifically designed to respond quickly and handle high air volume with minimal wear, even in harsh environments.
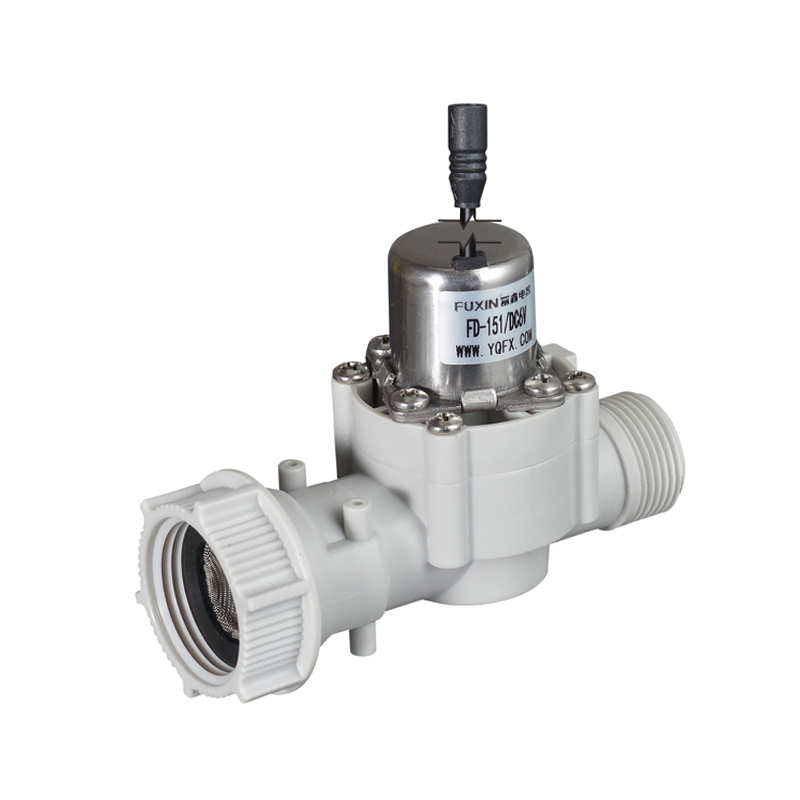

Compared to continuously energized solenoid valves, the Pulse Solenoid Valve offers a more robust and cost-effective solution for industrial cleaning systems. Its simple but powerful design reduces maintenance needs and supports longer service intervals. Additionally, the use of high-performance materials—such as corrosion-resistant aluminum bodies and durable rubber diaphragms—makes the Pulse Solenoid Valve suitable for use in environments with abrasive dust or moisture.
From a technical standpoint, the distinction between pulse activation and continuous energization is more than a matter of power consumption. It influences the entire control logic of the system, the lifespan of the coil, and the responsiveness of the valve under variable pressures. This is why the Pulse Solenoid Valve is often chosen for operations where timing, durability, and efficiency must be finely balanced.
In conclusion, understanding how the Pulse Solenoid Valve works provides valuable insight into its essential role in industrial air filtration and pneumatic control. Its reliance on momentary electromagnetic force for rapid actuation sets it apart from conventional valve technology, making it a reliable component in systems where precision and reliability are critical. As industry demands cleaner, more energy-efficient processes, the Pulse Solenoid Valve continues to serve as a key enabler of smart dust control and air management solutions.

 EN
EN English
English Español
Español